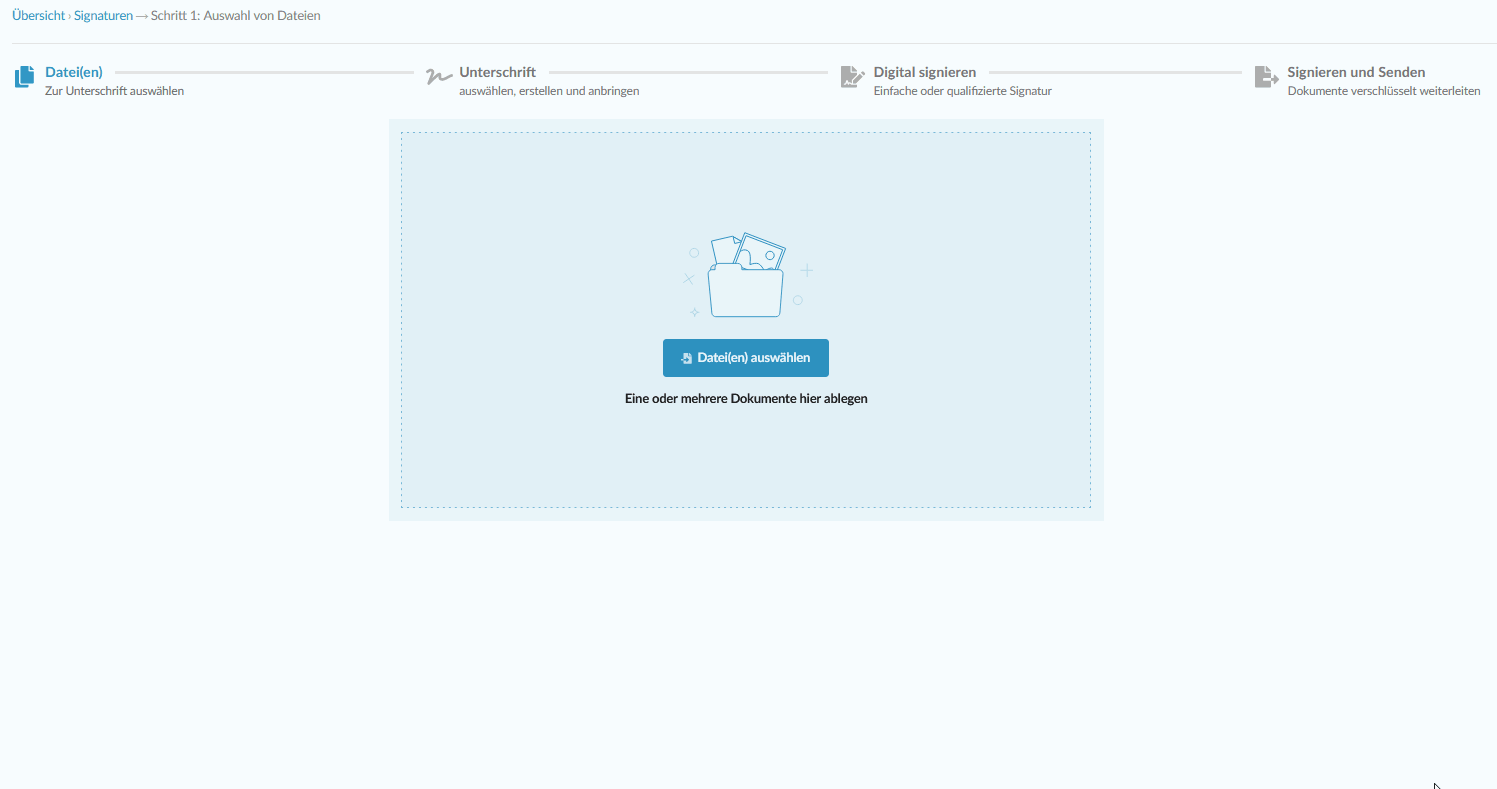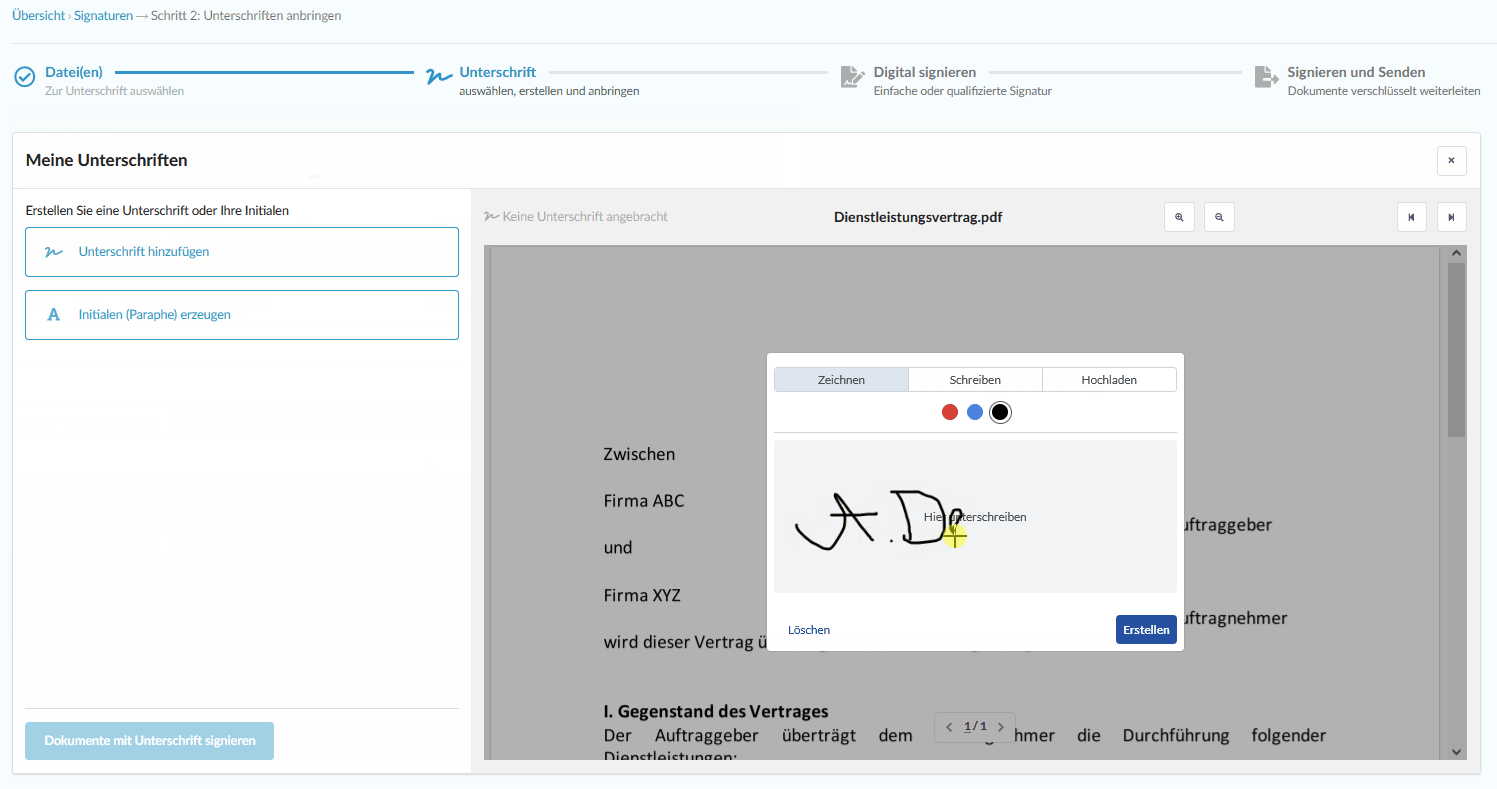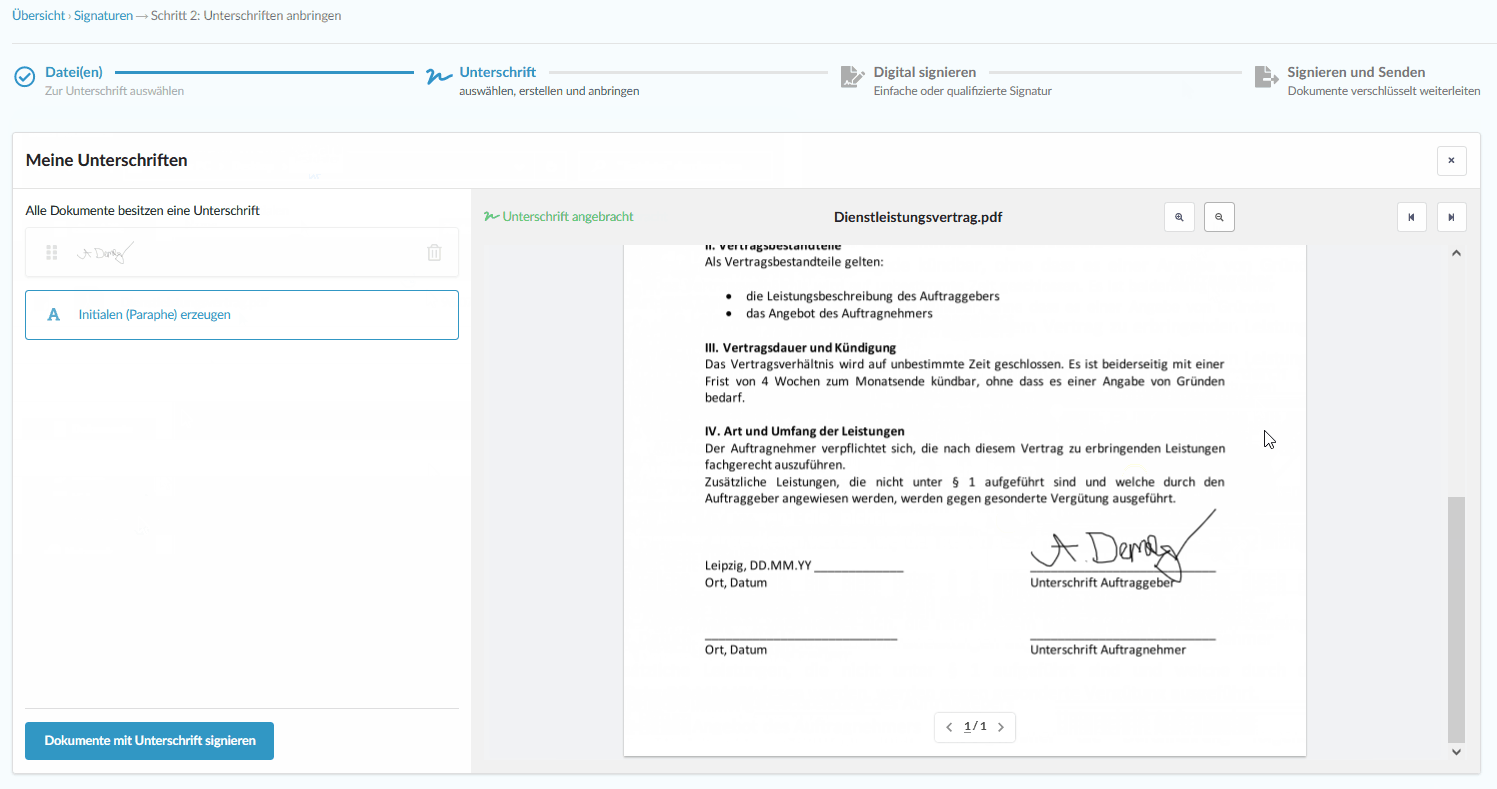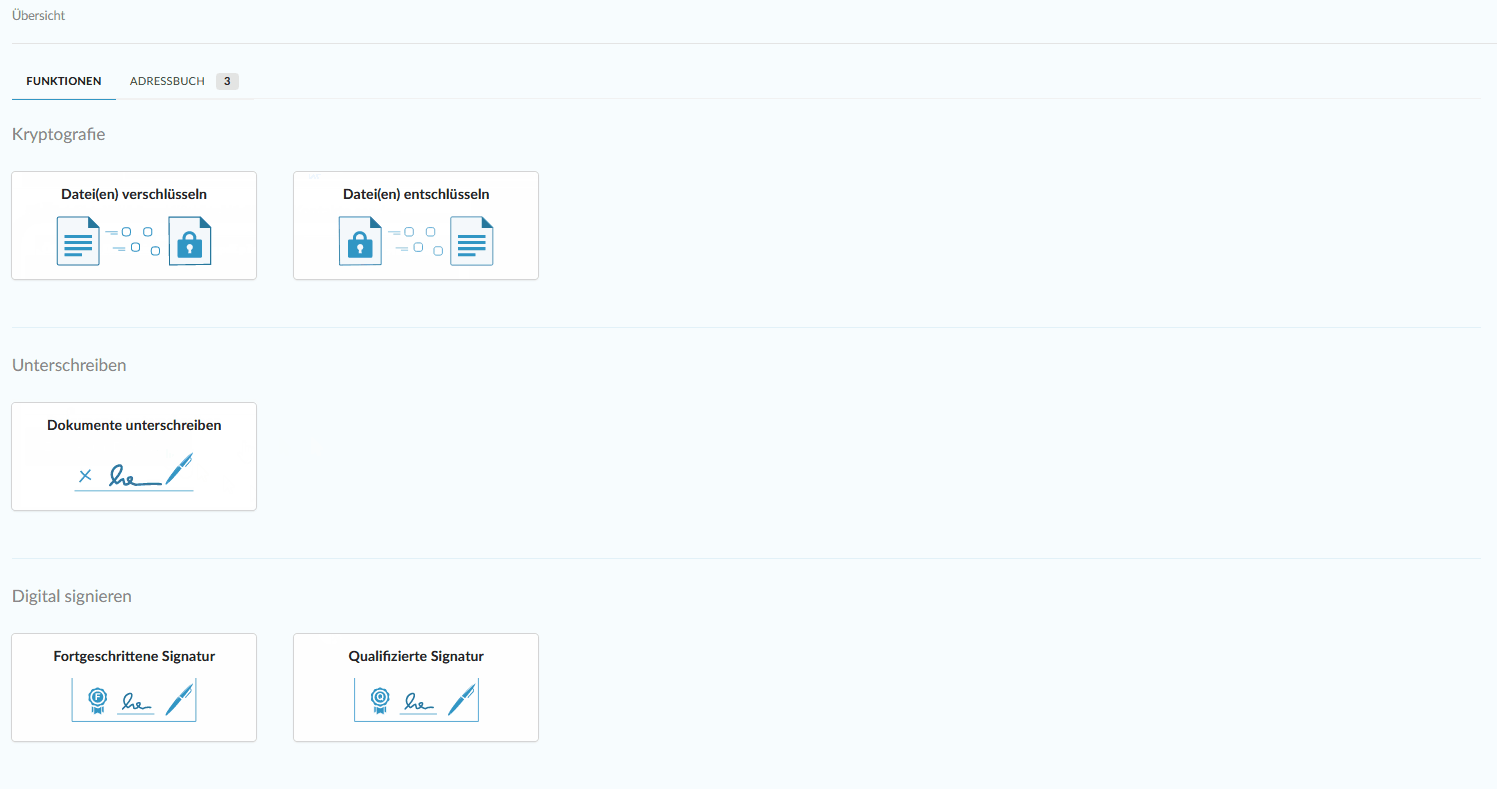
Add your simple, advanced and qualified digital signature without hardware
WIE EINFACH SIE DIGITAL UNTERSCHREIBEN KÖNNEN, ZEIGT DIE FOLGENDE ANIMATION:
Digital signature at the click of a mouse
Digital signature - Your advantages
Combine the advantages of simple signatures with secure cryptography with proTECTr
proTECTr signature forms
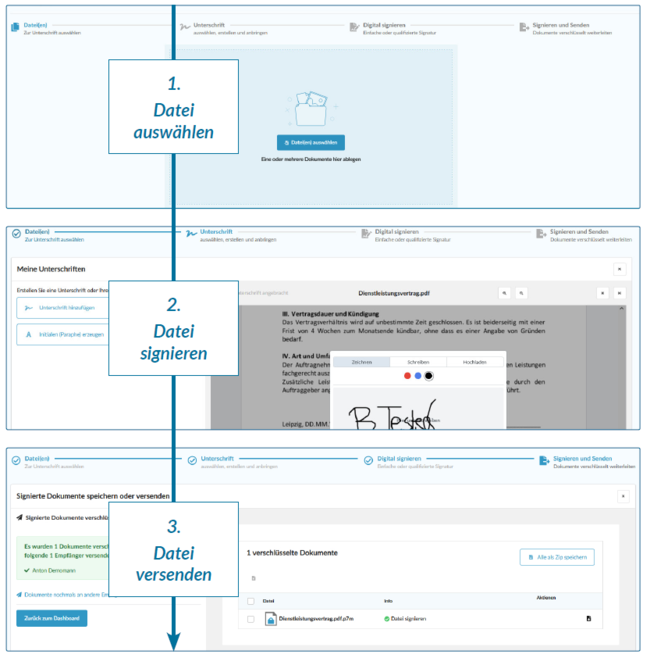
proTECTr offers a range of options for signing digitally. Which form is the right one is decided by the acceptance of the parties involved. Only if the written form is required, the qualified electronic signature must always be used.
To make the differences clear, the cryptographic forms of the electronic signature are separated conceptually:
| proTECTr Bezeichnung | Signaturform | Identitätslevel |
|---|---|---|
Signature | Simple electronic signature | ID-Level 1 |
Signature | Advanced electronic signature1 | ID-Level 2 |
Signature | Qualified elektronic signature1 | ID-Level 3 |
- Fortgeschrittene Elektronische Signatur
- Qualifizierte Elektronische Signatur
- Simple Electronic Signature
 Simple electronic signature
Simple electronic signature
A simple signature is simple and quick to use. For example, it can consist of a textual name in an e-mail or a scanned signature. The simple electronic signature is the weakest form of signature because it can be executed without identity verification. This means that it cannot be clearly assigned to a person or the signatory. Therefore, this type of signature should only be used when there is a low legal risk, such as for the following documents:
- General business relations
- Documentation
- Internal protocols
- PDF with scanned signature
 Advanced electronic signature
Advanced electronic signature
The advanced electronic signature enables the signatory to be identified and is uniquely assigned to the signatory. It must be created with a unique, secret signature key to which only the holder has access. The advanced signature therefore offers a higher level of evidential value and security than the simple signature. Thus, this signature can be used for the following documents:
- Data privacy statements
- Permanent employment contracts (without digital evidence)
- Insurance applications
- SEPA mandates
- Powers of attorney
- Non-disclosure agreements
 Qualified electronic signature
Qualified electronic signature
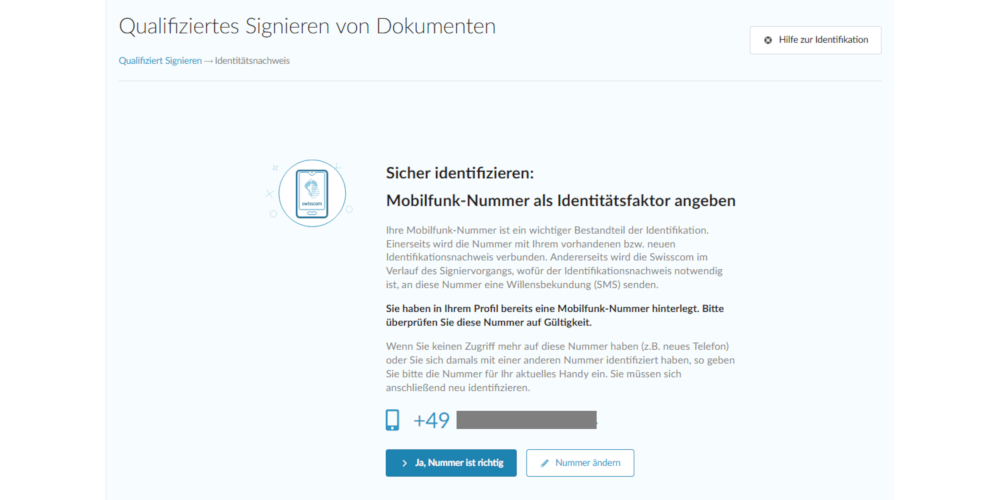
The qualified electronic signature offers the highest evidential value for digital signatures and is thus equivalent to a handwritten signature. This level of security requires the identity of the person signing to be verified, for example via video or bank ident. After successful verification, a certified trust service provider creates an electronic certificate with the name of the signer. With this certificate and a signature creation device (QSCD), the signer can trigger a qualified signature.
A qualified signature can therefore replace a handwritten signature and be used for documents where a written form requirement is necessary, such as:
- Clause on the limitation of the term of employment contracts (fixed-term employment contracts)
- Unlimited employment contracts (with digital evidence value)
- Guarantees
- Life insurance policies
Use all forms of electronic signature with the proTECTr Business account
Creating a qualified remote signature with proTECTr - How it works
Frequently asked questions about the digital signature
Depending on its characteristics, the digital signature can fulfil two basic tasks. On the one hand, it provides proof of authorship, comparable to a handwritten signature on paper. On the other hand, it can be used, especially in cryptographic forms, to determine whether a piece of digital information has been changed after the time of signature. In other words, signatures protect the integrity of data and can be used to prove manipulation.
The different types of signatures offer different probative value and security for the protection of files and documents. A distinction is made between simple, advanced and qualified signatures. The legal framework conditions are standardised in the European eIDAS Regulation for the internal market and implemented in national law with the Trust Services Act.
Electronic signatures offer companies and organisations the possibility to implement business processes that are already digitally designed today without media discontinuity. So whenever a personal signature is required to minimise business risks, paper, pen and stamp can be put aside with it. The digital signing of documents saves time, costs and resources, and mailing can be replaced and accelerated by secure electronic communication.
The electronic signature is considered a generic term and refers to data in electronic form that serves for authentication. This can be a digitised handwritten signature, but also the very secure qualified electronic signature.
According to the BSI, a digital signature is an electronic signature based on cryptographic algorithms. It thus offers the doubtless assignment of the signature to the signatory. Basically, users need an electronic certificate with associated keys to generate the signature. The value or quality of the signature then depends on the status of the issuer of these certificates. Thus, advanced certificates can be generated at different points by the users themselves. For the highest form, one turns to so-called trust service providers who, in accordance with the eIDAS Regulation, generate the certificate generation in a security-checked process and also store it on secure hardware (HSM)
The advanced and the qualified electronic signature are considered digital signatures.
SIMPLE electronic signature
A simple signature is simple and quick to use. It can, for example, consist of a textual name in an e-mail or a scanned signature. The simple electronic signature is the weakest form of signature because it can be executed without identity verification. This means that it cannot be clearly assigned to a person or the signatory and offers no protection against manipulation. Therefore, this type of signature should only be used for documents with a low legal risk, such as the following:
- General business relationships
- Documentation
- Internal protocols
- PDF with scanned signature
ADVANCED
The advanced electronic signature enables the identification of the signatory and is uniquely assigned to him. It must be created with a unique, secret signature key to which only the holder has access. The advanced signature therefore offers a higher degree of evidential value and security than the simple signature and also very good protection against manipulation. Thus, this signature can be used for the following documents:
- Data protection declarations
- Unlimited employment contracts (without digital evidence value)
- Insurance applications
- SEPA mandates
- Powers of attorney
- Confidentiality agreements
QUALIFIED
The qualified electronic signature provides the highest level of evidential value in digital signatures, making it equivalent to a handwritten signature. This level of security requires the identity of the person signing to be verified by the issuer of the certificate, for example by video or bank ident. After successful verification, a certified trust service provider creates an electronic certificate with the name of the signatory. With this certificate and a secure signature creation device (QSCD), the signer can trigger a qualified signature.
The qualified signature can thus replace a handwritten signature and be used for documents where a written form requirement is necessary, such as:
- Clause for the limitation of the term of employment contracts (fixed-term employment contracts)
- Indefinite employment contracts (with digital evidence value)
- Guarantees
- Life insurance
In the past, the application of cryptography in everyday life was often complicated and posed considerable problems for the normal user. For example, a signature card, a suitable reader and additional software had to be procured for a qualified electronic signature. In general terms, the higher the security requirement, the greater the effort and the lower the acceptance. With the eID, the user has to be able to access his or her personal data.
The eIDAS Regulation and the introduction of the so-called remote signature have remedied this situation. This opens up possibilities for achieving user-friendly embedding in existing processes in addition to the use of specialised cloud solutions such as proTECTr. In order to reduce the previous additional cryptographic effort to an acceptable minimum and to relieve the user of it as much as possible, security technologies are integrated into the applications frequently used by the users.
This means that the security technologies can be integrated into existing processes in a user-friendly way. In concrete terms, the user should not have to worry about whether an electronic consent has the same value as a signature on a paper form when concluding a contract online. The necessary components are already included in proTECTr.
In addition, proTECTr meets further user-friendly criteria:
- mobile and trusted use from the cloud
- once-only registration of secure identities
- Omission of additional hardware
When considering signatures, the connection between signature generation and signature verification should always be seen.
Since a simple electronic signature is not a digital signature in the cryptographic sense, i.e. it can neither be generated cryptographically nor verified accordingly, a verification result reflects the subjective knowledge of the verifier. The legal value of such a signature is accordingly low.
Electronic signatures are generated in several steps with the help of special cryptographic software. On the one hand, this software has the task of calculating a unique document image (hash value). Secondly, this hash value is then encrypted with the private key of the corresponding certificate. In this way, data is linked to the selected certificate during the signature process.
The verification of electronic signatures is also carried out by special cryptographic software. Once again, a one-to-one document image is calculated and compared with the hash value of the signature. If both values match, the data in the document has not been changed (manipulated). In this way, the integrity of the data is proven.
In addition, the validity of the assigned certificate must be checked. Depending on the use case and the form of the signature, the trust anchors for this can be different. For qualified certificates, however, trust services are prescribed according to eIDAS. For qualified certificates, these trust services additionally confirm the identity of the certificate holder and thus the authorship of the data.
According to the eIDAS Regulation, all signature types are legally valid and enforceable. Ultimately, the users determine the accepted level of signature among themselves. Due to the different levels of evidential value of electronic signatures, only the qualified signature can replace the handwritten signature in the case of a written form requirement. In contrast to all others, the qualified form creates a so-called reversal of the burden of proof. This means that a plaintiff must prove that the qualified signature is invalid.
To generate an electronic signature, you need a commercially available computer, laptop or comparable device. Furthermore, you need a corresponding signature application component, the signature generation software, which in the case of proTECTr is easy to use as a SaaS/Cloud solution. Furthermore, an electronic certificate corresponding to the use case with associated key material is necessary. Only in the case that certificate and key are stored on a smartcard, a card reader is necessary as additional hardware.
It is always interesting to use it when business processes are to run completely digitally and a minimum of legal certainty is required. Although a contract can in principle be concluded with a handshake, many companies fix it on paper and have the parties involved sign it. If paper is omitted, an electronic signature should be used. If the written form is required, the qualified electronic signature should be used.
One use case is, for example, distributed working methods across several locations, where enormous time savings and resource conservation are possible.